Python version history is a testament to one of the successful yet pioneering programming languages. Like other programming languages, Python has transformed how developers use code in this digital era. The language started in the early 90s and has made leaps and bounds in the last three decades.
The journey was not smooth by any stretch of imagination, as Python underwent massive transformations and enhancements over the years.
Python Version History Over the Years (A Snapshot)
Through its previous and latest versions, Python has made considerable progress. These versions help the popular language deliver advanced capabilities, minimizing the effort and difficulty of coding.
- 2025 (Python 3.13.5): This latest version, Python 3.13.5, has impressed users with its enhanced optimizations and improved capabilities. Users can benefit from impressive features like enhanced interactive interpreter, a preliminary and experimental JIT, and more.
- 2024 (Python 3.13.2): This version delivered new features along with an experimental JIT compiler. Furthermore, this stable release comprised performance improvements.
- 2023 (Python 3.12): This version concentrated on performance specifically. New features enhanced its impact.
- 2000 (Python 2.0): This version incorporated List comprehension, allowing data to be processed easily.
- 1994 (Python 1.0): Python 1.0 included exception handling and modules while introducing built-in lambda and reduced functions and mapping and filtering functions in its system.
Python Version History (Latest and Previous Versions)

Python’s inspiring history dates back to the early 1990s. This section will highlight the impacts of Python version history by describing various Python releases and versions under one roof.
Python 3.14.0a5 – Alpha Version (2025)
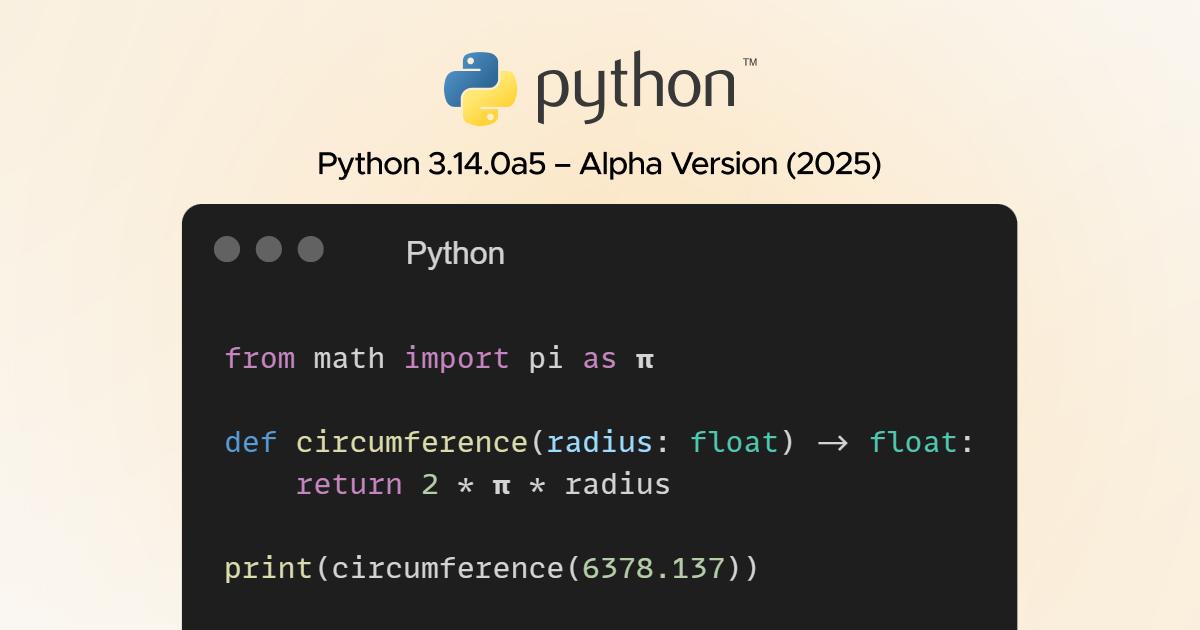
The latest version of Python is 3.14.0.a.5. The good thing about this Python latest version is an array of impactful features, including deferred evaluation of annotations, template strings, better error messages, a “Tail-call-compiled” interpreter, A C API for Python runtime configuration, etc.
Python 3.13 (2024)
This release of Python 3.13 brought more optimizations and features, continuing the language’s evolution. As far as the new features are concerned, users can experience an advanced yet interactive interpreter, JIT (Just-In-Time) compiler (PEP 744), and a free threaded mode (PEP 703).
Python 3.12 (2023)
In 2023, Python latest release was 3.12. Python 3.1.2 offered an impressive blend of features and optimizations, such as enhanced error messages, flexible Python f-string, type parameter syntax, module improvement, and syntactic formalization of f-strings.
Python 3.11 (2022)
Python 3.11 enhanced developer experience and performance by introducing new features, such as improved error messages, Exception Groups, Exception Notes, and crucial speed gains (10-60% faster).
Python 3.10 (2021)
Users enjoyed impressive features while utilizing one of the major Python releases, Python 3.10. These features included parenthesized context managers, pattern matching, and more. The former provided support for numerous context managers in a single with statement, while the latter focused on matching complex data structures.
Python 3.9 (2020)
As per the history of Python, Python 3.9 focused on enhancing the language, offering features like string methods, dictionary merge and update operators, and more. In addition, users experienced other features, such as pattern matching, the zoneinfo module, improved type hinting, and more.
Python 3.8 (2019)
Python 3.8 is known among users for launching new optimizations and features like positional-only parameters and the walrus operator. Positional-only Parameters suggest that arguments must be passed positionally. Similarly, the walrus operator refers to the assignment expression that enables developers to assign a value to a variable. Furthermore, developers smartly utilized the same value within the expression simultaneously.
Python 3.7 (2018)
Python 3.7 did help improve performance and offered new features like Data Classes and Context Variables. Data classes helped generate special approaches, such as __init__ and __repr__ in classes. Besides, Context Variables allowed developers to manage context-local state.
Python 3.6 (2016)
Python 3.6, Python latest version then, comprised various improvements, such as formatted string literals (f-strings), asynchronous generators, and underscores in numeric literals. The first improvement helped developers include expressions inside string literals. The underscores in numeric literals specifically enhanced the readability of large numbers. The last feature improved asynchronous programming.
Python 3.5 (2015)
Python 3.5 focused explicitly on fulfilling the needs of contemporary programming by delivering features such as type hints, async, and await. The former helped add type annotations to function return values and arguments. The other feature supported asynchronous programming by making async code easily readable and manageable.
Python 3.4 (2014)
The Python history reveals that this version became popular among users due to several key improvements, such as Asyncio and Pathlib. Asyncio is a framework that helps developers write asynchronous programs that support concurrent code execution. Likewise, Pathlib is an impactful Python standard library.
Python 3.0 or Python 3000 (2008)
Python 3000, or Python 3.0, or Py3k, erased redundant constructs and inconsistencies from Python 2.x. Users were fortunate to use various enticing features, such as New Syntax and Semantics, Removal of Deprecated Features, Print Function, and more.
Python 2.7 (2010)
According to the history of Python, Python 2.7 was the last significant release in the Python 2.x series. This version offered users helpful features like Improved Syntax, Set Literals, and Ordered Dictionaries.
Python 2.0 (2000)
Python 2.0 was another significant release. It offered the foundation for contemporary Python with powerful features like Unicode Support, List Comprehensions, and Garbage Collection.
Python 1.5 (1997)
Python 1.5 concentrated on offering crucial updates, such as Unicode Support and Standard Library Enhancements. The former provided users with support for Unicode and facilitated internationalization. The other feature expanded the standard library and made Python a versatile language.
Python 1.0 (1994)
The first official release that paved the way for one of the prominent programming languages was Python 1.0. It arrived in the market through fascinating features like Exception Handling, Lambda, Map, Filter, and Reduce. The first Python version revolutionized data manipulation and improved code error management and exceptions.
The above Python version list demonstrates the success of one of the remarkable programming languages in the last three decades.
Python Version History Comparison
This section will compare different Python versions, including the current and previous ones.
Python 1.0 vs. Python 2.0
| Feature | Python 1.0 | Python 2.0 |
|---|---|---|
| Release Type | It was the first and one of the oldest official Python releases. | Offered new features and improvements. |
| Key Features | It comprised basic programming constructs. | It included list comprehensions and improved garbage collection. |
| Feature Set | Nominal features compared to modern Python | Still nominal compared to the latest Python versions. |
| Backward Compatibility | Being the first version of the Python language, it was not backward-compatible. | Backward compatible with Python 1.0 for easier migration. |
Python 2.7 vs. Python 3.0
| Feature | Python 2.7 | Python 3.0 |
|---|---|---|
| Release Type | It is a final release in the Python 2.x series. | It was one of the crucial Python releases with reasonable changes. |
| Usage | Users utilized the previous version of Python for several years. | Improvements for language consistency were made in this version. |
| Key Features | The support was provided to users for Python 2.x. | The default Unicode support helped remove idiosyncrasies. |
Python 3.5 vs. Python 3.8
| Feature | Python 3.5 | Python 3.8 |
|---|---|---|
| Key Features | It is a final release in the Python 2.x series and is considered one of the old versions of Python. | It was one of the crucial Python releases with reasonable changes. |
| Focus Area | Users utilized the previous version of Python for several years. | Improvements for language consistency were made in this version. |
| Common Improvements | The support was provided to users for Python 2.x. | The default Unicode support helped remove idiosyncrasies. |
Python 3.9 vs. Python 3.13
| Feature | Python 3.9 | Python 3.13 |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | This Python version offered reasonable performance without boosting speed. | Python 3.11 was over 50% faster than previous Python releases, while Python 3.12 is 5% faster. |
| New Syntax Features | It did not have structural pattern matching. | This version focused on incorporating match and case statements for pattern matching purposes. |
| Error Reporting | This Python previous version included basic error messages. | This version comprised enhanced error messages with helpful information. |
Can We Use Python for WordPress?
There is no denying that WordPress primarily relies on PHP. You can consider using Python in WordPress through custom integrations, such as Python scripts with server-side or external APIs. As you might know, Python current version is 3.13.5.
Wrapping Up
We hope you like our blog post explaining the history of the Python version. As you know, the versions demonstrate Python’s growth over time and the significance of Python version history. Each new or latest version of Python validates this point significantly.
All these versions and Python releases help improve the performance and scalability of one of the leading programming languages.


















































