There is no denying that removing a directory in Linux is relatively easy if you use the GUI. In another instance, you can still remove or delete directories using terminal commands if you can’t access the GUI.
This blog post will describe how to remove a directory in Linux using commands in the terminal window or command line.
What Are the Prerequisites for Removing a Directory in Linux?
Here are a few prerequisites or requirements you must fulfill before you remove directories in Linux:
- You must have a computer or a device that runs an operating system based on Linux.
- You must have an account that offers sudo privileges.
- You should easily access the terminal window or command line when deleting directories in Linux.
Why Should We Use rmdir?
The rmdir command in Linux can remove or delete empty directories. This command is ideal for deleting a directory containing no files or subdirectories. In short, rmdir makes the directory removal process efficient and straightforward, specifically when managing temporary directories and cleaning empty folders.
What Should We Do to Remove a Directory in Linux with the rmdir Command?
You should follow the steps below to remove a directory in Linux using the rmdir command:
- Launch the Terminal application on your Linux device, which is located in the application menu.
- Use the cd command to go to the directory containing the empty directory you wish to delete.
For example, if the directory you want to remove resides at ~/parent_dir/empty_dir, write the following command:
cd ~/parent_dir
- Verify or authenticate the directory’s content. For this purpose, you should change Is to Is empty_dir to list the directory content you want to remove.
- You should remove the directory, but ensure you correctly mention the path/file name of the target directory. Once you are sure about deleting the target directory and its content, use the rm command along with the -r (recursive) option:
rm -r empty_dir
This command lets you smartly remove or delete the directory and its content.
- At this point, you should proactively check for any errors if found. You will not receive any output if you have removed the directory correctly. That said, rmdir will showcase an error message highlighting the reason for the failure if the directory is not empty or it does not have the required permissions.
- Once you have executed the rmdir command, check if the directory has been deleted. To do this, you should use the Is command to list the directory’s content. Once the directory has been deleted successfully, you will not find it in the list.
Now, you should use the command below to authenticate the directory removal, taking advantage of the Is command:
ls ~/parent_dir
You should replace “~/parent_dir” with the path to the parent directory where the deleted directory resided. If the directory has been removed, it will not appear in the content list.
What Should We Do to Remove a Directory in Linux with the rm Command?
If you want to remove a directory in Linux with the rm command, here is what you should do:
- Launch the Terminal application on your Linux device.
- Navigate to the parent directory, which is the directory you wish to delete, using the cd command. For instance,
cd ~/dir_to_delete
- Verify or authenticate the directory’s content, ensuring you delete the correct directory. This lets you confirm that no crucial subdirectories or files are removed. Use the “ls”command to list the directory content:
ls
- Use the rm command plus the -r (recursive) option to remove the directory and its content:
rm - r dir_to_delete
- If you successfully remove the directory, you will not receive any output. If it is not, permission issues or errors will appear as error messages.
- Once you have executed the rm command, you must confirm directory removal by listing the directory’s content:
ls
Crucial rm and rmdir Command Options Users Should Know
Here are various rm and rmdir command options you must know when deleting a directory in Linux, including files and folders:
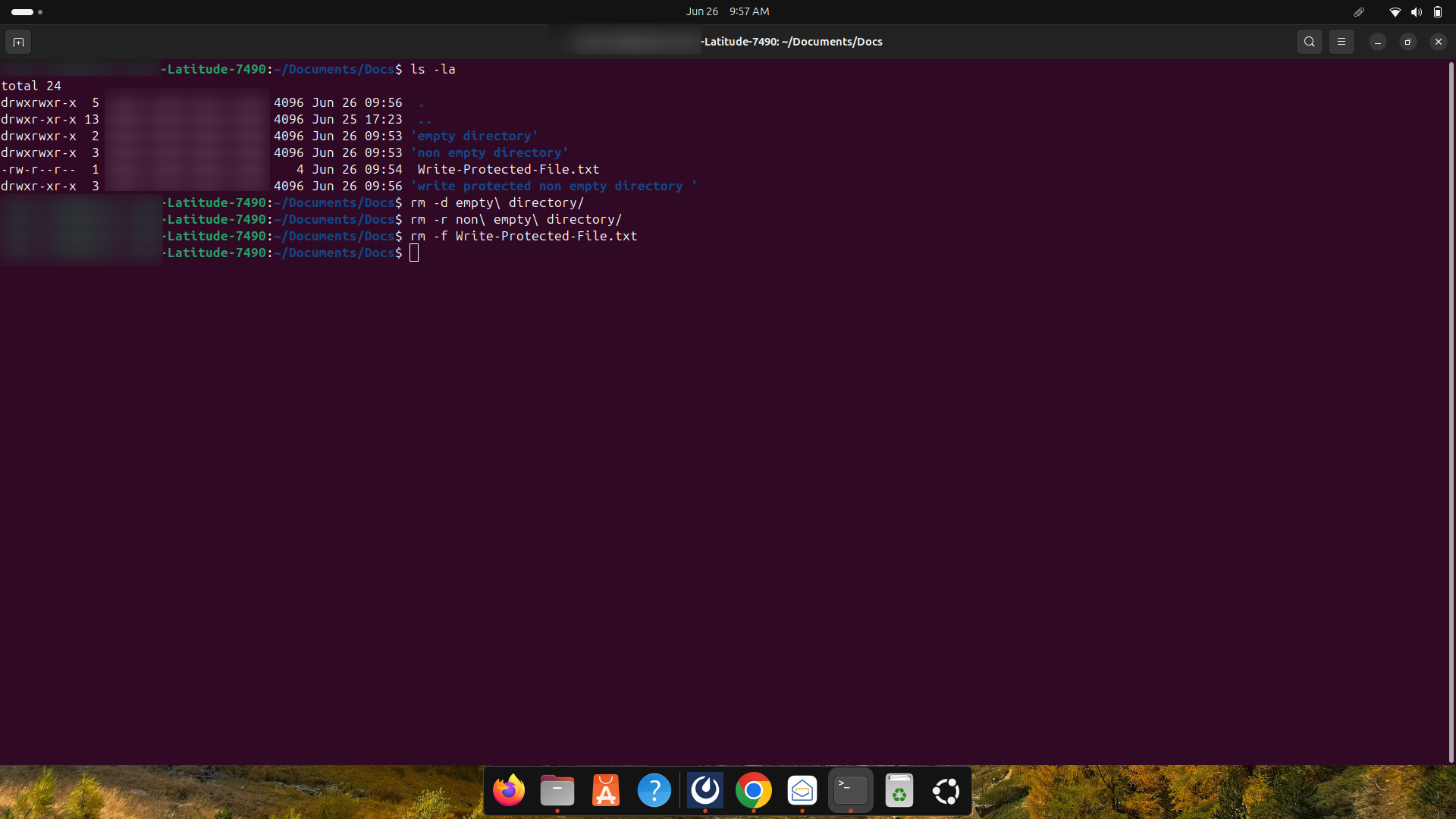
- rm -d: It helps remove the empty directory with the help of the rm command.
- rm -r: It helps remove or delete a non-empty directory and its content.
- rm -f: It lets users overlook any prompt when removing a write-protected file.
- rm -rf: Users can overlook any prompt when removing a write-protected non-empty folder.
- rm -i: Users will see a confirmation prompt before every removal.
- rm ?: A wildcard that depicts a single character.
- rmdir -p: Delete the empty subdirectory and its parent directory.
- rm *: A wildcard that depicts multiple characters.
- rmdir -v: It helps print the information indicating that the specified directory was removed.
What are the Key Differences Between rm and rmdir?
As you know, these commands help remove directories in Linux. However, they have varied objectives.
rmdir
- It helps remove or delete empty Linux directories.
- It doesn’t allow users to delete a directory that comprises subdirectories or files.
- It helps clean empty directories.
rm
- It helps remove files and directories and is more convenient.
- It allows users to remove directories and their contents recursively.
- It lets users delete directories comprising subdirectories or files.
Is the Phrase “remove Directory Linux” Correct?
Luckily, the phrase “remove directory Linux” is correct, and users often use it. It is a phenomenon in which a directory is removed or deleted in the Linux operating system. Moreover, prominent commands like the rm or rmdir commands play a key role in deleting a directory and its content.
Does the Linux Version History Affect the Directory Removal Process?
The Linux version history does not influence the directory removal or deletion process. Users must utilize the rm and rmdir commands when removing a directory in Linux. These commands are key to core utilities and are accessible in all Linux versions.
Understanding Linux Directories
Directories are a vital part of the file system hierarchy in Linux. They primarily work as containers for files and other directories. Each directory has a specific name and can simultaneously store various subdirectories and files. Linux directories allow users to organize their files and directories.
What Are the Key Differences Between Files and Directories?
As you know, files and directories are the key part of the Linux file system. However, they differ from each other due to different functions.
Files
Files contain information or data, such as images, programs, or text documents. They have uncommon names within directories and contain permissions, ownership, and file type. Files are easily changeable; users can delete them depending on their privileges and permissions.
Directories
A directory, or a folder, helps organize files and other directories but doesn’t store data directly. It primarily functions as a structure to organize the file system. Furthermore, it plays a crucial role when grouping related directories and files, making file system management easier.
Directories can save files and other directories and develop a hierarchical structure, reflecting the system’s data organization. Like files, directories have ownership and permissions, determining who can use, change, or delete them.
Wrapping Up
Removing a directory in Linux is not as difficult as it seems. We expect you to appreciate our blog post, which thoroughly explains how to do so. Before deleting directories or files using your Linux devices, understand the rm and rmdir commands first.
This will help you perform the directory removal process correctly. The former helps remove files and folders, while the latter is suitable for deleting empty directories. Hopefully, you can easily follow the above blog post and remove a directory in Linux.





















































