Cross-site scripting (XSS) is a popular exploitation technique that enables scammers to execute arbitrary code on a compromised website. Through cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks, hackers can insert malicious code into WordPress sites, thereby gaining access to sensitive data.
This blog post will describe cross-site scripting (XSS) and discuss how XSS attacks work in WordPress. It will also explain how to safeguard your website against WordPress cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks using various preventive methods.
What Does Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Mean?
Cross-site scripting (XSS) is a serious security vulnerability that allows hackers or scammers to inject malicious code into web pages that other users view. The scammers insert code snippets into a site’s HTML, which alter how the browser communicates with the page.
XSS attacks often monitor user interactions and target them when needed. Various examples of user interactions include posting comments, clicking links, submitting forms, and other similar actions.
How Does a Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Attack Work in WordPress?

Unfortunately, XSS is one of the leading website security attacks. However, the website owners, developers, and other stakeholders do not understand the consequences of such attacks. Regarding the WordPress XSS attack, scammers exploit existing cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities to their full advantage. They inject harmful scripts into WordPress sites, targeting user input fields such as contact forms, comment sections, URL parameters, and search bars.
For instance, they can incorporate a script into a comment box. The WordPress database usually contains this comment box, and sadly, when a visitor lands on the post, the script is executed in the visitor’s browser. Consequently, the script either steals their session cookie or redirects them to a malicious website.
More importantly, Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks can lead to a website defacement. These attacks enable hackers to manipulate the targeted sites’ images, text, and other elements. Moreover, they can hide the current content, replacing it with their messages and different sections.
Entry Points for WordPress XSS Attacks
- Input Fields: User input fields, such as login, contact, search boxes, and login forms, are obvious entry points. Hackers can insert malicious scripts if an app does not validate or sanitize user input appropriately.
- Comments: Scammers can exploit user-generated comments on forums, social media platforms, and blogs. Furthermore, they can insert scripts if the application does not filter or escape user-generated content.
- URLs (Query Parameters): As you know, URL parameters can carry user input. Additionally, if an application directly reflects these parameters in the HTML response, it can be vulnerable to cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks.
- SVG Images: Unlike other images, SVG images are not fixed in size. SVG images are created with vector graphics. They are scaled up and down depending on the screen size. For that reason, they are rendered in users’ browsers, making them prone to XSS attacks.
Types of XSS Attacks
Cross-site scripting attacks are categorized depending on where the code is stored and executed. There are three key types of attacks: stored or persistent, reflected, and DOM. That said, they are not mutually exclusive by any stretch of imagination.
XSS attacks can combine these types. Understanding these types and seeing how they intersect is still helpful, though.
Reflected XSS
The malicious script originates from the current HTTP request in a reflected cross-site scripting (XSS) attack. In this type of XSS attack, a user clicks the suspicious link on the site. As a result, the server receives a request from the user’s browser that contains malicious code. Unfortunately, the server reproduces malicious or harmful code in the user’s browser.
Stored or Persistent XSS
In a stored XSS attack, the malicious script comes from the website’s database and is sent to users when they visit the targeted site. This is the reason it is called a stored or persistent XSS attack.
DOM-based XSS
In a DOM-based XSS attack, the vulnerability resides on the client rather than the server-side code. This advanced attack is complex and more challenging to detect. Additionally, it does not contain server communication.
What Should We Do to Avoid WordPress XSS Attacks?
Safeguarding against cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks is better than looking for a cure once attacks have occurred. Here are a few easy yet effective methods you can follow to safeguard your website against XSS attacks:
Update Plugins and Themes on Your Website
Do you know that your plugins and themes can have security vulnerabilities? Yes, it is true. These vulnerabilities often exist in different plugins and themes installed on your website. Therefore, you should update plugins and themes regularly, as they help install much-needed security patches released by plugin and theme developers.
Malicious actors can target your site with cross-site scripting (XSS) or SQL injection attacks if you do not regularly update plugins and themes. Sadly, these attacks share commonalities: They exploit security vulnerabilities by injecting malicious code.
Utilize a Web Application Firewall (WAF)
Installing a results-driven web application firewall can help protect your WordPress site. Thus, you must set up a firewall on your site, such as MalCare, Wordfence, Sucuri, Imperva, etc. They prevent malicious traffic from reaching your site.
Install a Security Plugin
Installing a security plugin can help protect your WordPress site from cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. For instance, you can easily install and activate numerous security plugins, such as Sucuri Security, Security & Malware Scan, and Security Optimizer, among others, without any fuss.
Unsurprisingly, XSS attacks are a significant security hassle for site owners, developers, and visitors. They can help scammers obtain login credentials, allowing them to harm sites through malware. In this situation, the security plugins mentioned above enable you to monitor unusual activity. They also help detect malware quickly and provide various removal methods.
Enforce Content Security Policy (CSP)
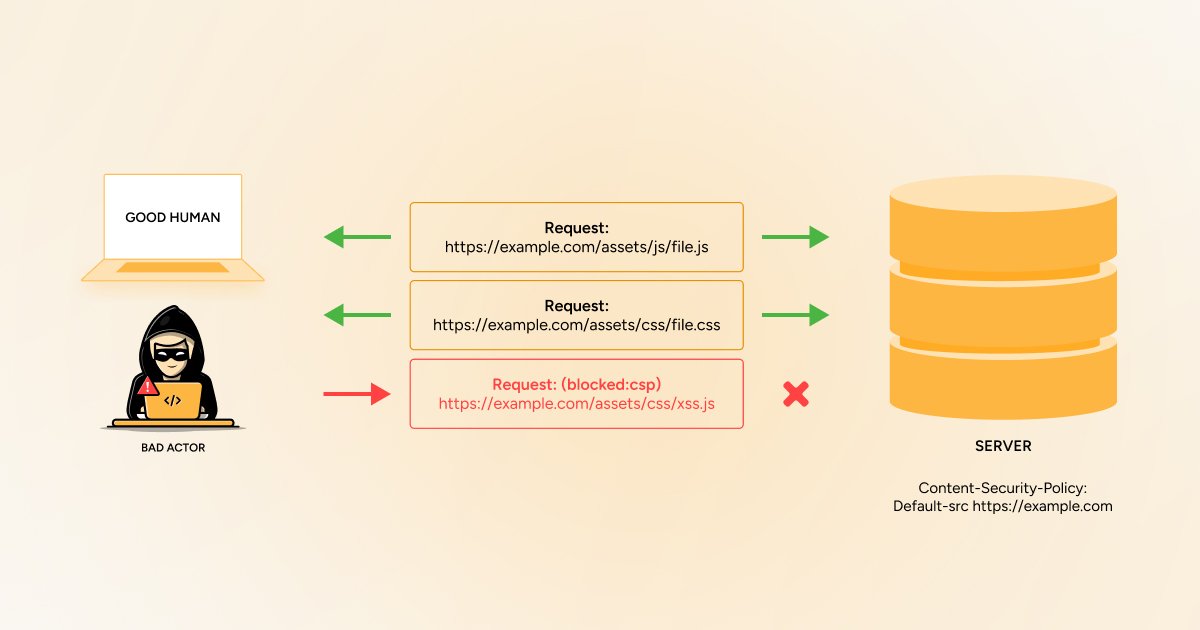
Content Security Policy (CSP) is a feature that enables site owners or developers to minimize the risk of several security threats. It usually comprises a series of instructions from a site to the browser that order the browser to implement limitations on various aspects of the site’s code that it can perform.
The main use case for CSP is to control which resources, specifically JavaScript resources, a document can load. Website owners and developers can use Content Security Policy (CSP) to protect websites against cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks.
Scammers can insert malicious code into victims’ WordPress sites through cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. Hence, it is essential to implement Content Security Policy (CSP) on the website to safeguard against Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks.
Consequences of WordPress XSS Attacks

WordPress XSS attacks can compromise the security of any website, leading to various consequences, including data breaches, reputational damage, SEO losses, financial losses, content defacement, and more.
Regarding data breaches, XSS attacks enable scammers to obtain sensitive information, including credit card data and passwords. Moreover, these attacks can negatively impact a business’s reputation, as they direct visitors to phishing websites.
XSS attacks can negatively affect any website’s SEO (Search Engine Optimization). Hackers can replace a website’s actual content with filthy and promotional messages. They can motivate users to click spammy links, compelling search engines to ban the site for endorsing dubious content.
Therefore, you must follow the above methods to protect your WordPress site from the adverse effects of cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks.
Wrapping Up
Cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks are among the most severe threats to website security. However, following the desired practices and tools can efficiently secure your site. In addition, you can smartly decrease the risk of WordPress XSS attacks by utilizing a Web Application Firewall, enforcing a Content Security Policy (CSP), and more.
These practices also help prevent SQL injections, another known attack that benefits from the vulnerabilities found in database queries. Additionally, you must implement several deterrence measures, such as regular code reviews, security audits, and staying up-to-date with contemporary security patches, which are crucial in maintaining a secure website environment.
In short, WordPress XSS attacks are not uncommon or unique. They help scammers target websites to steal and misuse sensitive data, such as passwords, credit card details, and other personal information.
As a diligent website admin, you must protect your visitors from risks and threats. Therefore, following the above methods can prevent your WordPress site from XSS attacks.