Every site, whether new or old, experiences security risks. Unfortunately, thousands of known security vulnerabilities make hackers and other cybercriminals’ jobs easy, as they can easily target their desired websites.
In this situation, understanding what website hardening is and why it is necessary will allow you to ensure your website remains safe and productive.
This blog post will describe website hardening and different ways you can follow to safeguard your WordPress website.
What Do You Mean by Website Hardening?
The phrase “website hardening” means you must take various proactive measures to secure your WordPress site. It is about adding a protection layer that helps reduce the attack risk. In short, website hardening allows site owners to improve their sites’ security to the next level. It comprises settings, configurations, approaches, and techniques to enhance a site’s security.
Website Hardening – 18 Best Ways to Secure Your WordPress Site
Your website’s security is crucial for keeping your business data safe and building trust and credibility with your website visitors. This is one of the key questions businesses of all sizes ask when assessing WordPress.
Fortunately, you have multiple options to enhance and protect the security of your website. These options include:
1. Remove the Default WordPress Admin Account
Hackers and other cyber terrorists usually target the default WordPress admin account. To increase the WordPress website’s security, the username must be complex. Furthermore, they can consider deleting the default admin account.
Before removing the default admin account, you must create another administrator account using the new username. The new account can then be easily used to access your site.
2. Limit WordPress User Permissions
Website owners must limit user permissions to safeguard their sites against unforeseen issues. They should let users perform particular tasks and not give them full admin access if it is not essential.
3. Monitor the Site and Keep Up with Its Log Activity

Logs are crucial for website monitoring. They are also beneficial when troubleshooting technical issues or ensuring user accountability.
In addition, if you have a WooCommerce site, logs ensure PCI DSS compliance. Moreover, saving logs for future analysis is helpful for CIPA, GDPR, and other regulations. Therefore, you should check for irregularities in your website logs to identify important information related to malfunctions, attack attempts, misconfigurations, and other necessary status information.
4. Look For Input Sanitization Techniques
Input sanitization helps examine data on your sites and removes or “sanitizes” anything harmful. Website forms are the right option for an example of input sanitization. They sanitize input to avoid SQL injection attacks in WordPress.
When you apply input sanitization techniques, you must mention precisely what sort of data you expect from the user:
- Will you accept special characters?
- What is the maximum size or length?
- Will you only let numbers or letters?
Any visitor to your site can be a spammer or an attacker. Therefore, it’s essential to exercise caution and not trust information input into website fields. Hence, you should check what is sent to your application or site.
This will allow you to improve your security considerably, safeguarding sites against SQL injections. You should not forget that accidental damage can harm your site as much as intentional damage.
5. Consider Using Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication requires numerous authentication methods from several categories of credentials to authenticate a user’s identity. It comprises two or more independent authentication forms, including password, security token, and biometrics. Combining these authentication forms can create a layered defense, making it difficult for unauthorized attackers to breach.
WordPress users can use multiple plugins to help achieve this on their websites. Select one with solid reviews and ensure the development team regularly maintains and patches it.
6. Practice the Principle of Least Privilege
Restrict each team member’s ability to do things and ensure they don’t have more privileges than necessary. To achieve this objective, you must practice the principle of least privilege.
Giving every user administrative access is a security threat. You can reduce this risk by using appropriate permissions. In this scenario, you must use CMS roles and explain access control for your website.
For instance, if an author or editor writes or works for your website, they do not require administrator privileges.
Grant each employee the exact amount of access needed to do their job. Then, remove users and revoke access when they no longer need it.
7. Mitigate Exposure of Information
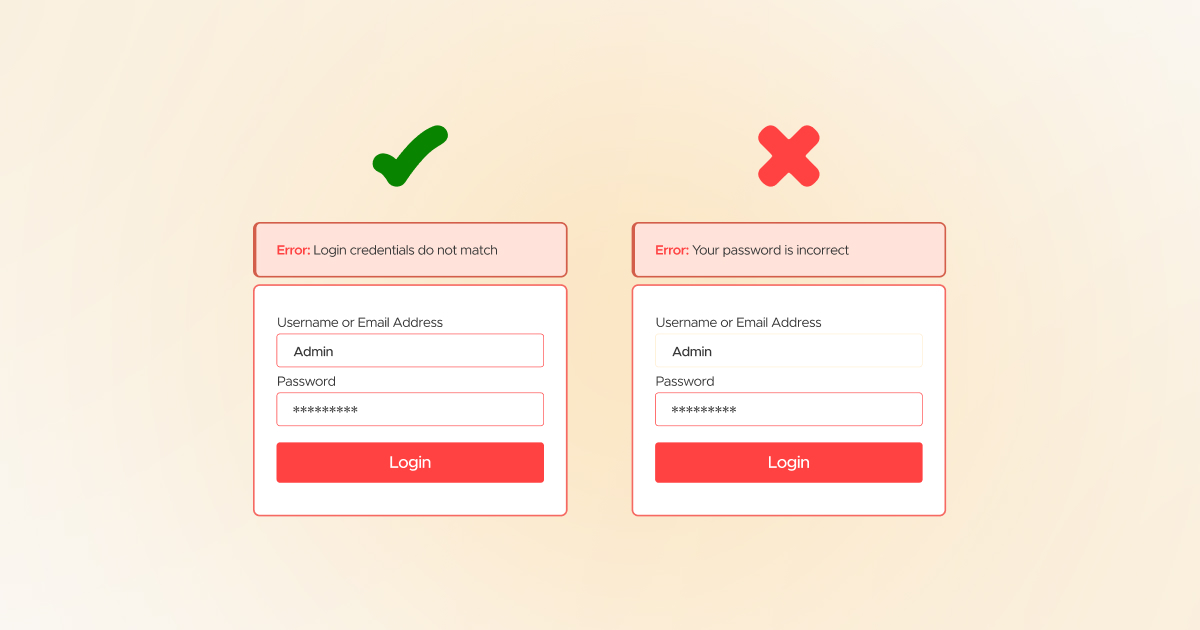
You must change failed password attempt messages to “Login credentials do not match” or “Login credentials are invalid.” Furthermore, don’t show this failed password attempt message like, “Your password is incorrect.”
That’s because in this example, you explain to the attacker that the username is correct. However, the password needs to be accurate, so do not give a hint or clue to hackers or attackers in any way. This reduced verbosity can lessen the chance of an impactful brute force attack.
Furthermore, ensure sensitive website data is not written to the server or site logs, and that logs should not be publicly accessible. An internal error code can reduce the information displayed while permitting easy debugging.
8. Deactivate File Editing
Unfortunately, hackers can access your site after accessing a WordPress Administrator account. Using the dashboard, they can alter the coding of your plugins and themes by clicking the “Editor” option. Similarly, hackers can upload scripts to showcase their content and spam users. Likewise, they can deface your website, significantly harming users’ security.
To manually deactivate file editing, use the FTP client or cPanel. Moreover, you can consider utilizing a file manager plugin.
NOTE: If you use the file manager plugin, uninstall it afterward. You should not use it regularly, as it can be a threat.
9. Set Alerts for Suspicious WordPress Logins
Monitoring your website for suspicious logins is necessary. It will enable you to identify and avert attacks. Thus, you should use a plugin like Login SMS Alert to obtain alerts when users log in from an unknown IP address or location. To complement this, tools like Aura’s digital footprint checker can help uncover exposed personal or business information that may be used in targeted attacks.
10. Auto Logout Inactive Users
You must log out inactive users automatically from your WordPress website. Doing so allows you to safeguard your site from hackers, as they can target the site for unauthorized access. In this situation, you should utilize a plugin like Inactive Logout that logs users out automatically after a specified inactivity period.
11. Deactivate User Registration
Registration is typically disabled by default to prevent public users from registering on your WordPress website.
However, to confirm user registration is deactivated, go to the Settings > General page in your WordPress dashboard area, then navigate to the Membership section. You must ensure that the checkbox next to “Anyone can register” is not selected.
12. Implement a Content Security Policy (CSP)
A CSP is a set of rules that dictate how resources on a web page can be loaded and executed. It is instrumental in avoiding various attacks, such as the infamous Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks, where hackers insert malicious scripts into websites and other users view them.
Applying a CSP ensures that only content from trusted sources can be executed, restricting attackers’ ability to exploit web application vulnerabilities. In addition, it offers website administrators granular control over the different resources a web page can access and interact with, such as scripts, images, fonts, and forms.
Having a CSP in place can help alleviate clickjacking attacks. In this instance, the attacker tries to trick visitors into pressing something different from what they intended. A CSP can impose strict guidelines describing which domains the browser should consider safe for fetching resources, minimizing the risk of content injection attacks.
13. Hide the WordPress Version
A few WordPress releases depict the CMS version you use by default in the website’s footer. The website visitors can overlook the WordPress version. That said, it can be dangerous to make this information public.
If your business uses an outdated WordPress version, attackers can target it using specific exploits. Since your website publicly shows this information, the job of those attackers becomes much simpler.
Newer versions of the CMS don’t show this information on the front end. If your website displays it, this means that you use an outdated version of WordPress. This harms your website, so update the WordPress version immediately.
14. Add Password Protection to /wp-admin
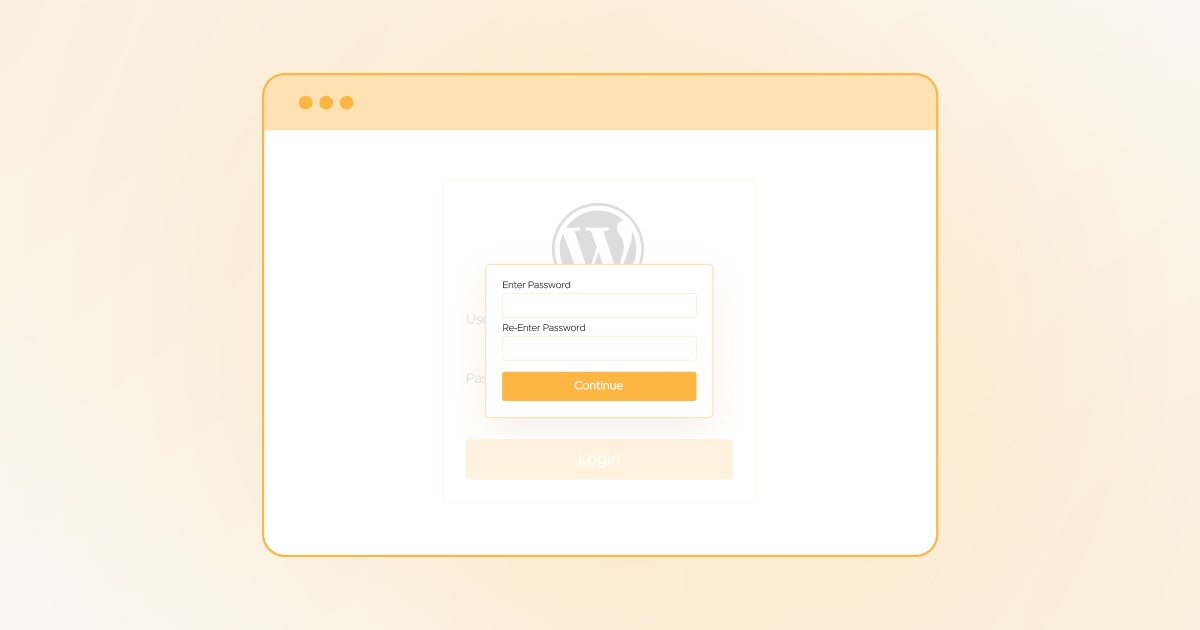
Website owners must consider adding password protection to the wp-admin login page. This will prevent attackers from easily accessing the login screen. Unfortunately, attackers or hackers can access the login screen if they misuse the internal credentials. In another case, they can access the login screen if the site owners have not configured other security measures.
Hence, you must safeguard the admin page or dashboard using an additional password. This will help you secure your site from numerous risks or attacks. When attackers access /wp-admin, the browser will require a secondary password via the pop-up.
If hackers or attackers do not know the password, they cannot access the admin screen. You can apply this security measure to your WordPress website through .htaccess. You will share the passwords among users. It does not offer the desired security level, but this added layer will help harden your WordPress site’s security.
15. Limit Access to the WordPress Files
Limiting access to the WordPress files is crucial and helps improve the WordPress site’s security. This process restricts access to key files such as .htaccess, wp-config.php, and the wp-content folder.
You must protect these files, as they contain sensitive information, such as login credentials, user and payment information, the site’s configuration, and more. Interestingly, you can change WordPress file permissions on your server, which can easily limit access to such files. Any user on the server can read WordPress files. That’s because these files are set to be readable.
That said, you can modify the WordPress file permissions when restricting access to such files to particular groups and users.
16. Change the Default WordPress Login URL
As you know, the WordPress login page is placed at /wp-admin. Sadly, spammers and other cybercriminals can target this page to accomplish their notorious objectives. Therefore, you must change the default WordPress login URL to keep hackers, spammers, and other cyber goons at bay.
For this purpose, you can benefit from a WordPress plugin, such as WPS Hide Login. Once you have installed and activated this plugin, navigate to Settings > WPS Hide Login and search for the “Login URL” field. You must write the new URL you wish to use as the login page. For example, you can consider using mydomain.com/yourlogin or mydomain.com/customlogin.
17. Back Up Your Website Frequently

You must back up your site frequently. This will help you activate the store version if anything unexpected happens or goes wrong. You can back up your website without fuss using the WordPress backup plugins, including Updraft Plus, BlogVault, etc.
You must access your WordPress files with an FTP client for a manual backup. Remember to copy all the files to a secure location. You can also export the database using phpMyAdmin.
18. Contact Website Development Agency
Sometimes, contacting a website development agency can help you secure your WordPress website regarding the issue of site hardening in the right direction.
For this purpose, you can hire WPExperts, a results-driven website development agency that uses contemporary website development approaches and solution-oriented tactics to serve small and large businesses worldwide.
What Should We Do to Secure Our WordPress Website for Free?
When hardening a WordPress website’s security, consider using an SSL certificate. Luckily, you can use a free or a paid SSL certificate to beef up your site’s security, depending on your budget. As you know, SSL is commonly called Secure Sockets Layer.
The effectiveness of these security certificates lies in their application. This means that users’ activities on your site determine the efficacy of an SSL certificate.
What Do You Mean by Harden WordPress or Hardening WordPress?
Harden WordPress, or hardening WordPress, helps apply various security measures to prevent data breaches or cyberattacks and safeguard a WordPress site.
The security measures applied in WordPress hardening comprise technical configurations and best practices to mitigate the risks of vulnerabilities, which can hamper your website’s confidentiality, availability, and integrity.
Wrapping Up
Website hardening is one of the main steps site owners, developers, and other stakeholders must take to safeguard their WordPress sites from cyber threats.
The above website hardening techniques, such as limiting access to WordPress files, adding password protection to /wp-admin, applying a Content Security Policy (CSP), limiting WordPress user permissions, and more, can reduce security threats to a certain extent.
Remember that website hardening is a continuous phenomenon; therefore, you must monitor your site’s performance proactively. This will ensure you offer site users a secure and meaningful WordPress experience.


















































